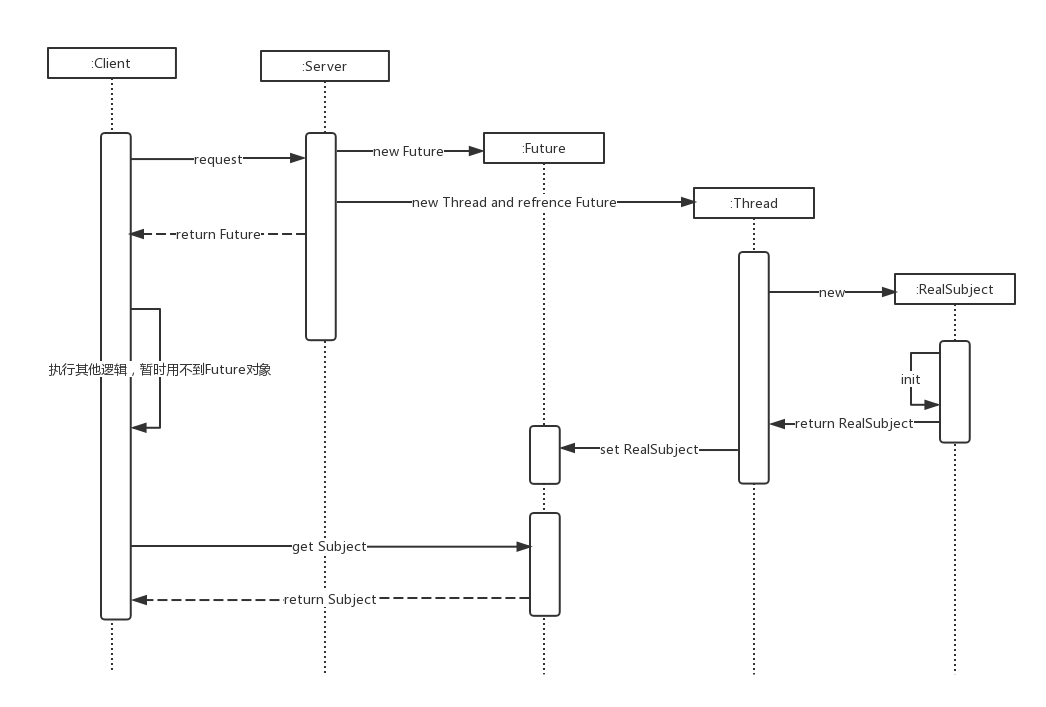
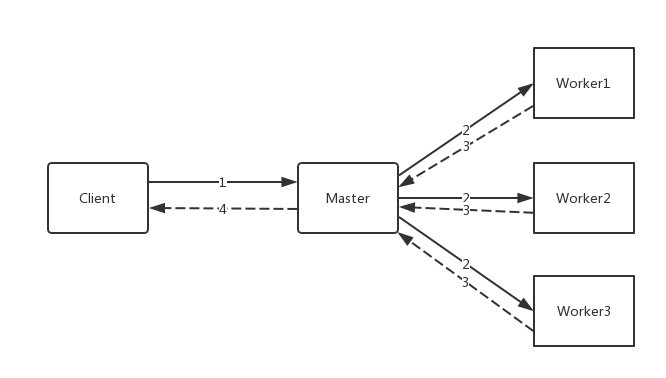
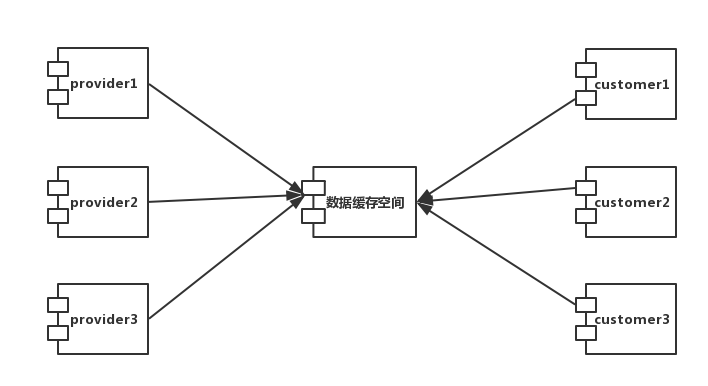
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| 当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:1, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:2, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2, 获取了数据,id为:3, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:4, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 1
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:5, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 2
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 5
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 3
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2, 获取了数据,id为:6, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:7, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:8, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 7
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:9, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:10, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:11, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:12, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 8
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 4
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 10
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:13, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 6
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:14, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2, 获取了数据,id为:15, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2, 获取了数据,id为:16, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 12
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 11
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:17, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:18, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 9
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2, 获取了数据,id为:19, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 13
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:20, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 16
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 14
当前线程:pool-1-thread-3, 获取了数据,id为:21, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 18
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 15
当前线程:pool-1-thread-1, 获取了数据,id为:22, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前线程:pool-1-thread-2, 获取了数据,id为:23, 进行装载到公共缓冲区中...
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 17
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 21
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 19
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-5, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 22
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-6, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 20
当前消费线程:pool-1-thread-4, 消费成功,消费数据为id: 23
|