1、单Selector问题
对于并发不是很大的情况下,一个Selector负责轮询注册事件的变化,并对事件进行处理,是没有问题的。但是当并发比较大的时候,客户端连接比较多,且IO也比较多的情况,一个Selector肯定是不能满足对于系统性能的要求。
对于高并发的情况,给去的解决方案是:分为boss(一个或多个)和worker(多个)两种线程来处理,每一个线程都拥有自己的Selector。boss线程负责接收客户端请求,将accept到的SocketChannel转交给其中的一个worker线程去处理IO请求。
结合上一篇文章的图解,这一篇实现的效果,类似于:
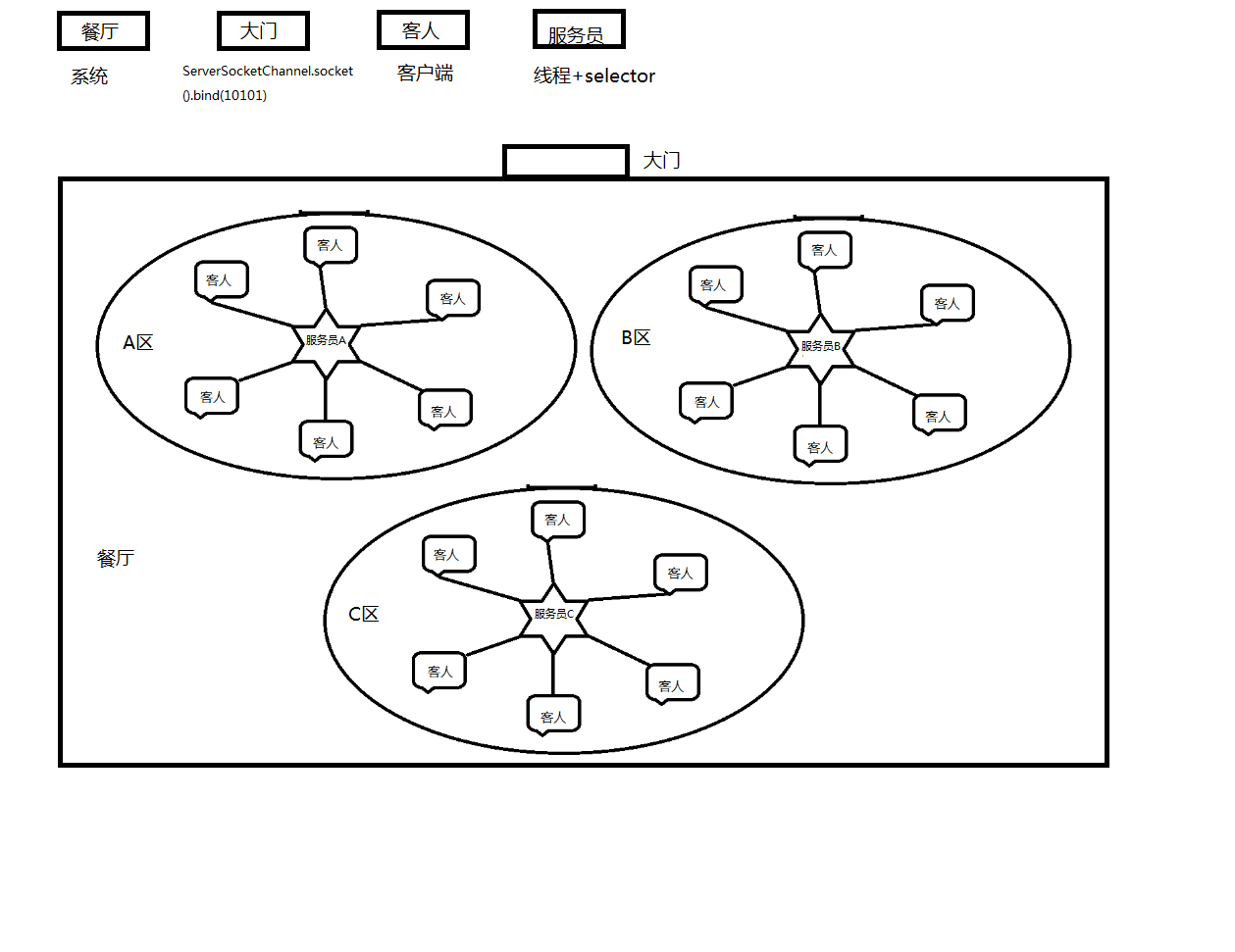
通俗解释:用餐高峰期,餐厅客人较多,一个服务员肯定是忙不过来的,这个时候就需要多个服务员来接待客人了。
2、代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| package com.example.part_02_nio.demo002;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class Pool {
private final AtomicInteger bossIndex = new AtomicInteger();
private Boss[] bosses;
private final AtomicInteger workerIndex = new AtomicInteger();
private Worker[] workeres;
public Pool(Executor bossExecutor, Executor workerExecutor) throws IOException {
initBoss(bossExecutor, 1);
initWorker(workerExecutor, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2);
}
private void initBoss(Executor bossExecutor, int count) throws IOException {
this.bosses = new Boss[count];
for (int i = 0; i < bosses.length; i++) {
bosses[i] = new Boss("boss thread " + (i+1), this);
bossExecutor.execute(bosses[i]);
}
}
private void initWorker(Executor workerExecutor, int count) throws IOException {
this.workeres = new Worker[count];
for (int i = 0; i < workeres.length; i++) {
workeres[i] = new Worker("worker thread " + (i+1));
workerExecutor.execute(workeres[i]);
}
}
public Worker nextWorker() {
return workeres[Math.abs(workerIndex.getAndIncrement() % workeres.length)];
}
public Boss nextBoss() {
return bosses[Math.abs(bossIndex.getAndIncrement() % bosses.length)];
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
| package com.example.part_02_nio.demo002;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
public class Boss implements Runnable{
private String threadName;
private Pool pool;
private Selector selector = Selector.open();
private AtomicBoolean blocking = new AtomicBoolean(true);
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Runnable> taskQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public Boss(String threadName, Pool pool) throws IOException {
this.threadName = threadName;
this.pool = pool;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().setName(threadName);
while(true) {
try {
blocking.set(true);
selector.select();
processQueue();
processEvent();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void processQueue() {
while(true) {
Runnable task = taskQueue.poll();
if(task == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":从任务队列中执行任务");
task.run();
}
}
private void processEvent() {
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
if(selectedKeys == null || selectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if(key.isAcceptable()) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":获取到客户端连接事件");
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":将客户端连接转交给worker去处理");
this.pool.nextWorker().registSocketChannel(socketChannel);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void registServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
if(this.selector != null) {
taskQueue.offer(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
while(blocking.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
this.selector.wakeup();
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
| package com.example.part_02_nio.demo002;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
public class Worker implements Runnable{
private String threadName;
private Selector selector = Selector.open();
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Runnable> taskQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public Worker(String threadName) throws IOException {
this.threadName = threadName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().setName(threadName);
while(true) {
try {
selector.select(500);
processQueue();
processEvent();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void processQueue() {
while(true) {
Runnable task = taskQueue.poll();
if(task == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":从任务队列中执行任务");
task.run();
}
}
private void processEvent() {
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
if(selectedKeys == null || selectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if(key.isReadable()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":获取到客户端写入事件");
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int read = channel.read(byteBuffer);
if(read > 0) {
byte[] bs = byteBuffer.array();
String msg = new String(bs).trim();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":获取到客户端写入信息——" + msg);
ByteBuffer responseBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(("response:" + msg).getBytes());
channel.write(responseBuffer);
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":客户端已经关闭连接");
key.cancel();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void registSocketChannel(SocketChannel channel) {
if(this.selector != null) {
taskQueue.offer(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| package com.example.part_02_nio.demo002;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Executor bossExecutor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Executor workerExecutor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Pool pool = new Pool(bossExecutor, workerExecutor);
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8899));
pool.nextBoss().registServerSocketChannel(serverChannel);
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel2 = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel2.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel2.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8889));
pool.nextBoss().registServerSocketChannel(serverChannel2);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| package com.example.part_02_nio.demo002;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 16;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(count);
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
final int index = i;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
latch.countDown();
latch.await();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", index / 2 == 0 ? 8899 : 8889);
SocketChannel sc = null;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(address);
sc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(("请求" + index).getBytes()));
buffer.clear();
int read = sc.read(buffer);
if (read > 0) {
byte[] data = buffer.array();
String msg = new String(data).trim();
System.out.println("客户端端收到信息:" + msg);
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sc != null) {
try {
sc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
|
3、测试结果
server端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
| boss thread 1:从任务队列中执行任务
boss thread 1:从任务队列中执行任务
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
boss thread 1:获取到客户端连接事件
boss thread 1:将客户端连接转交给worker去处理
worker thread 1:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 2:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 4:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 3:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 4:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 5:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 6:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 1:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 2:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 4:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 5:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 6:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 3:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 8:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 7:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 6:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 5:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 6:获取到客户端写入信息——请求9
worker thread 3:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 3:获取到客户端写入信息——请求6
worker thread 6:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 1:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 4:获取到客户端写入信息——请求3
worker thread 1:获取到客户端写入信息——请求12
worker thread 7:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 3:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 1:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 3:获取到客户端写入信息——请求2
worker thread 1:获取到客户端写入信息——请求10
worker thread 1:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 1:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 2:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 2:获取到客户端写入信息——请求14
worker thread 2:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 2:获取到客户端写入信息——请求15
worker thread 2:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 8:从任务队列中执行任务
worker thread 5:获取到客户端写入信息——请求5
worker thread 8:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 5:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 5:获取到客户端写入信息——请求8
worker thread 5:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 5:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 2:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 1:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 1:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 5:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 5:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 8:获取到客户端写入信息——请求4
worker thread 2:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 2:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 8:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 8:获取到客户端写入信息——请求16
worker thread 7:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 3:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 3:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 3:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 3:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 6:获取到客户端写入信息——请求1
worker thread 4:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 7:获取到客户端写入信息——请求13
worker thread 6:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 7:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 7:获取到客户端写入信息——请求11
worker thread 7:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 7:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 8:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 7:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 7:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 6:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 4:获取到客户端写入信息——请求7
worker thread 6:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 6:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 8:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 4:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 4:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 4:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 4:客户端已经关闭连接
worker thread 8:获取到客户端写入事件
worker thread 8:客户端已经关闭连接
|
client端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| 客户端端收到信息:response:请求6
客户端端收到信息:response:请求9
客户端端收到信息:response:请求3
客户端端收到信息:response:请求10
客户端端收到信息:response:请求12
客户端端收到信息:response:请求2
客户端端收到信息:response:请求14
客户端端收到信息:response:请求15
客户端端收到信息:response:请求5
客户端端收到信息:response:请求8
客户端端收到信息:response:请求4
客户端端收到信息:response:请求16
客户端端收到信息:response:请求1
客户端端收到信息:response:请求11
客户端端收到信息:response:请求13
客户端端收到信息:response:请求7
|
结果分析:
- 一个Selector可以注册多个channel,如代码中的boss就注册了两个ServerSocketChannel,分别为8899和8889
- 一个系统中可以存在多个Selector,代码中每一个boss/worker线程,都拥有一个Selector
- 通过结果输出可以看出,客户端的IO请求被均匀的分配到各个worker线程去处理,boss只是负责接收连接